  Leipzig: Thomaskirche II
|
IntroductionThe organ currently in the west end gallery of the Thomaskirche in Leipzig was built in 1889 by Wilhelm Sauer (1831-1916) of Frankfurt an der Oder and installed as part of a general renovation of the church.196 The 63-stop instrument had cone-valve windchests and mechanical action, and it was housed in an oak case built by a local woodworker named Arnemann. In 1902 Carl Piutti, the organist of the Thomaskirche, requested some changes, and Sauer added pneumatic action, three frei Kombinationen (combination pistons), an electric blower, and two stops. He also made some changes in voicing at this time. After Karl Straube became organist in 1902 (following the death of Piutti in June), he began discussing further changes with Sauer. As a result, in 1908 Sauer added 23 new stops with additional windchests and a new console. Changing taste during the decades following Straube's tenure (which ended in the 1920's) resulted in tonal modifications to the instrument followed by an extended period of neglect. Restoration of the Sauer organ was begun in 1988 by Christian Scheffler, who worked for the Frankfurt Organ Company, the successor to the Sauer firm. Scheffler has reconstructed original mixtures and some of the other altered stops, and plans have been made for the complete restoration of the organ to its 1908 disposition.
Organ Disposition |
| Manual I | Manual II | Manual III | Pedal | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principal | 16 | Salicional |
16
|
Lieblich Gedackt |
16
|
Majorbass | 32 | ||||||||
| Bordun |
16
|
Gedackt | 16 | Gamba | 16 | Untersatz | 32 | ||||||||
| Principal | 8 | Principal | 8 | Principal | 8 | Contrabass | 16 | ||||||||
| Geigenprincipal | 8 | Schalmei | 8 | Viola | 8 | Principal | 16 | ||||||||
| Viola di Gamba | 8 | Salicional | 8 | Aeoline | 8 | Violon | 16 | ||||||||
| Gemshorn | 8 | Harmonika | 8 | Voix céleste | 8 | Gemshorn | 16 | ||||||||
| Dulciana | 8 | Dolce | 8 | Spitzfloete | 8 | Subbass | 16 | ||||||||
| Doppelfloete | 8 | Flûte harmonique | 8 | Flûte d'amour | 8 | Salicetbass | 16 | ||||||||
| Flûte harmonique | 8 | Konzertfloete | 8 | Gedackt | 8 | Lieblich Gedackt | 16 | ||||||||
| Flauto dolce | 8 | Rohrfloete | 8 | Gemshorn | 8 | Quintbass | 102/3 | ||||||||
| Gedackt | 8 | Gedackt | 8 | Quintatön | 8 | Offenbass | 8 | ||||||||
| Quintatön | 8 | Octave | 4 | Fugara | 4 | Principal | 8 | ||||||||
| Quinte | 51/3 | Salicional | 4 | Traversfloete | 4 | Cello | 8 | ||||||||
| Octave | 4 | Flauto dolce | 4 | Praestant | 4 | Gemshorn | 8 | ||||||||
| Gemshorn | 4 | Quinte | 22/3 | Quinte | 22/3 | Bassfloete | 8 | ||||||||
| Rohrfloete | 4 | Piccolo | 2 | Flautino | 2 | Dulciana | 8 | ||||||||
| Violini | 4 | Cornett III | Harmonia aetheria III | Octave | 4 | ||||||||||
| Octave | 2 | Mixtur III | Oboe | 8 | Flauto dolce | 4 | |||||||||
| Rauschquinte II | Cymbel III | Trompette harmonique | 8 | Contraposaune | 32 | ||||||||||
| Mixtur III | Tuba | 8 | Posaune | 16 | |||||||||||
| Cornett II-IV | Clarinette | 8 | Fagott | 16 | |||||||||||
| Scharf V | Trompete | 8 | |||||||||||||
| Gross-Cymbel IV | Clarine | 4 | |||||||||||||
| Trompete | 16 | ||||||||||||||
| Trompete | 8 | ||||||||||||||
| Manualkoppeln II/I, III/I, III/II Pedalkoppeln I/P, II/P, III/P Mezzoforte, Forte, Tutti, Rohrwerke Piano-, Mezzoforte-, Forte- und Tuttipedal mit Absteller Handrigister ab drei frei einstellbare Kombinationen Rollschweller mit Absteller Jalousieschweller für Manual III Röhrenpneumatik (Spiel- und Registertraktur) Manualumfang: C-a''' Pedalumfang:C-f' |
|||||||||||||||
Photographs
|
© 2000 AD James H. Cook

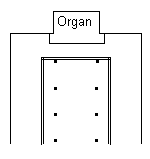 The case front was moved forward to its present position during the alterations of 1908. The floor plan and placement of columns in the building give the impression in this photograph that the building is narrow and tall. Look at the diagram to the right, which shows the floor plan of the west end of the nave in a simplified form. The small dots represent the first three or four of the columns that appear to be a wall in the photograph to the left. The double lines outline the gallery that not only extends across the west end of the nave but also extends along both sides. The church is actually rather wide, with sides equal in width to the center section of the nave, but the space is quite broken up (both visually and acoustically) by the large columns and galleries.
The case front was moved forward to its present position during the alterations of 1908. The floor plan and placement of columns in the building give the impression in this photograph that the building is narrow and tall. Look at the diagram to the right, which shows the floor plan of the west end of the nave in a simplified form. The small dots represent the first three or four of the columns that appear to be a wall in the photograph to the left. The double lines outline the gallery that not only extends across the west end of the nave but also extends along both sides. The church is actually rather wide, with sides equal in width to the center section of the nave, but the space is quite broken up (both visually and acoustically) by the large columns and galleries. The photograph to the right was taken from a different angle, and you can see how the organ gallery extends past the columns to the side walls of the nave. The corner of the organ gallery and the south wall gallery can also be seen.
The photograph to the right was taken from a different angle, and you can see how the organ gallery extends past the columns to the side walls of the nave. The corner of the organ gallery and the south wall gallery can also be seen.